Be punctual
Come first serve first
No cheating
Flora & Fauna
SPECIES NAME
 A
larger sized species, with a greyish colour and a prominent V-shaped snout.
Prefers brackish water, but also inhabits lower stretches of rivers and true marineenvironments. This is one of the rare species that
exhibits regular sea-going behaviour, which explains the great distribution
throughout the Caribbean. It is also found in hypersaline lakes such as Lago Enriquillo, in the Dominican Republic, which has one of the
largest populations of this species. Diet consists mostly of aquatic and terrestrial
vertebrates.
A
larger sized species, with a greyish colour and a prominent V-shaped snout.
Prefers brackish water, but also inhabits lower stretches of rivers and true marineenvironments. This is one of the rare species that
exhibits regular sea-going behaviour, which explains the great distribution
throughout the Caribbean. It is also found in hypersaline lakes such as Lago Enriquillo, in the Dominican Republic, which has one of the
largest populations of this species. Diet consists mostly of aquatic and terrestrial
vertebrates.
 A medium sized species with a narrow and elongated
snout. Lives in freshwater habitats within tropical forests of the continent.
Feeds mostly on fish but also other small to medium sized vertebrates.
Possibly belongs to its own monotypic genus, Mecistops. Insufficient data on conservation
A medium sized species with a narrow and elongated
snout. Lives in freshwater habitats within tropical forests of the continent.
Feeds mostly on fish but also other small to medium sized vertebrates.
Possibly belongs to its own monotypic genus, Mecistops. Insufficient data on conservation
 This
is a large species with a relatively elongated snout and a pale tan coloration
with scattered dark brown markings. Lives primarily in the Orinoco Basin. Despite having a rather narrow snout, preys on a wide
variety of vertebrates, including large mammals. It is a Critically Endangered species.
This
is a large species with a relatively elongated snout and a pale tan coloration
with scattered dark brown markings. Lives primarily in the Orinoco Basin. Despite having a rather narrow snout, preys on a wide
variety of vertebrates, including large mammals. It is a Critically Endangered species.
 A
smaller species with a narrow and elongated snout. It has light brown
coloration with darker bands on body and tail. Lives in river with considerable distance from the sea, to avoid
confrontations with saltwater crocodiles. Feeds mostly on fish and other small vertebrates.
A
smaller species with a narrow and elongated snout. It has light brown
coloration with darker bands on body and tail. Lives in river with considerable distance from the sea, to avoid
confrontations with saltwater crocodiles. Feeds mostly on fish and other small vertebrates.
 This is a relatively small species with a rather broader snout. It has heavy dorsal armour and a golden-brown colour that darkens as the animal matures. Prefers freshwater habitats and feeds on a variety of small to medium sized vertebrates. This species is Critically Endangered and the most severely threatened species of crocodile
This is a relatively small species with a rather broader snout. It has heavy dorsal armour and a golden-brown colour that darkens as the animal matures. Prefers freshwater habitats and feeds on a variety of small to medium sized vertebrates. This species is Critically Endangered and the most severely threatened species of crocodile
 A crocodile’s physical traits allow it to be a successful predator. Its external morphology is a sign of its aquatic and predatory lifestyle. Its streamlined body enables it to swim swiftly; it also tucks its feet
to the side while swimming, making it faster by decreasing water resistance.
Crocodiles have webbed feet which, though not used to propel them through the
water, allow them to make fast turns and sudden moves in the water or initiate
swimming. Webbed feet are an advantage in shallower water where the animals
sometimes move around by walking. Crocodiles have a palatal flap, a rigid tissue at the back of the mouth that
blocks the entry of water. The palate has a special path from the nostril to the glottis that bypasses the mouth. The nostrils are closed during submergence.
A crocodile’s physical traits allow it to be a successful predator. Its external morphology is a sign of its aquatic and predatory lifestyle. Its streamlined body enables it to swim swiftly; it also tucks its feet
to the side while swimming, making it faster by decreasing water resistance.
Crocodiles have webbed feet which, though not used to propel them through the
water, allow them to make fast turns and sudden moves in the water or initiate
swimming. Webbed feet are an advantage in shallower water where the animals
sometimes move around by walking. Crocodiles have a palatal flap, a rigid tissue at the back of the mouth that
blocks the entry of water. The palate has a special path from the nostril to the glottis that bypasses the mouth. The nostrils are closed during submergence.
Come first serve first
No cheating
Flora & Fauna
Crocodile
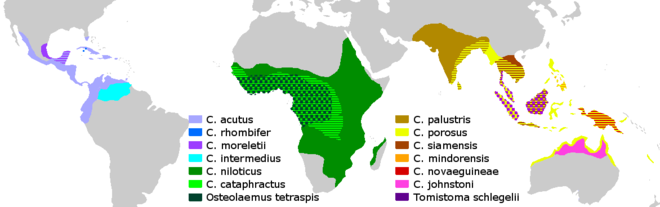
Crocodiles are large aquatic reptiles that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the Americas and Australia. Crocodylinae, all of whose members are considered true crocodiles, is classified as a biological subfamily. A broader sense of the term crocodile, Crocodylidae that includes Tomistoma, is not used in this article. The term crocodile here applies to only the species within the subfamily of Crocodylinae. The term is sometimes used even more loosely to include all extant members of the order Crocodilia, which includes the alligators and caimans, the gharial and false gharial (family Gavialidae), and all other living and fossil Crocodylomorpha.

SPECIES NAME
1. American crocodile (Crocodylus acutus)
 A
larger sized species, with a greyish colour and a prominent V-shaped snout.
Prefers brackish water, but also inhabits lower stretches of rivers and true marineenvironments. This is one of the rare species that
exhibits regular sea-going behaviour, which explains the great distribution
throughout the Caribbean. It is also found in hypersaline lakes such as Lago Enriquillo, in the Dominican Republic, which has one of the
largest populations of this species. Diet consists mostly of aquatic and terrestrial
vertebrates.
A
larger sized species, with a greyish colour and a prominent V-shaped snout.
Prefers brackish water, but also inhabits lower stretches of rivers and true marineenvironments. This is one of the rare species that
exhibits regular sea-going behaviour, which explains the great distribution
throughout the Caribbean. It is also found in hypersaline lakes such as Lago Enriquillo, in the Dominican Republic, which has one of the
largest populations of this species. Diet consists mostly of aquatic and terrestrial
vertebrates.  A medium sized species with a narrow and elongated
snout. Lives in freshwater habitats within tropical forests of the continent.
Feeds mostly on fish but also other small to medium sized vertebrates.
Possibly belongs to its own monotypic genus, Mecistops. Insufficient data on conservation
A medium sized species with a narrow and elongated
snout. Lives in freshwater habitats within tropical forests of the continent.
Feeds mostly on fish but also other small to medium sized vertebrates.
Possibly belongs to its own monotypic genus, Mecistops. Insufficient data on conservation This
is a large species with a relatively elongated snout and a pale tan coloration
with scattered dark brown markings. Lives primarily in the Orinoco Basin. Despite having a rather narrow snout, preys on a wide
variety of vertebrates, including large mammals. It is a Critically Endangered species.
This
is a large species with a relatively elongated snout and a pale tan coloration
with scattered dark brown markings. Lives primarily in the Orinoco Basin. Despite having a rather narrow snout, preys on a wide
variety of vertebrates, including large mammals. It is a Critically Endangered species.
4. Freshwater crocodile
 A
smaller species with a narrow and elongated snout. It has light brown
coloration with darker bands on body and tail. Lives in river with considerable distance from the sea, to avoid
confrontations with saltwater crocodiles. Feeds mostly on fish and other small vertebrates.
A
smaller species with a narrow and elongated snout. It has light brown
coloration with darker bands on body and tail. Lives in river with considerable distance from the sea, to avoid
confrontations with saltwater crocodiles. Feeds mostly on fish and other small vertebrates.
5. Philippine crocodile
 This is a relatively small species with a rather broader snout. It has heavy dorsal armour and a golden-brown colour that darkens as the animal matures. Prefers freshwater habitats and feeds on a variety of small to medium sized vertebrates. This species is Critically Endangered and the most severely threatened species of crocodile
This is a relatively small species with a rather broader snout. It has heavy dorsal armour and a golden-brown colour that darkens as the animal matures. Prefers freshwater habitats and feeds on a variety of small to medium sized vertebrates. This species is Critically Endangered and the most severely threatened species of crocodile
CHARACTERISTICS
 A crocodile’s physical traits allow it to be a successful predator. Its external morphology is a sign of its aquatic and predatory lifestyle. Its streamlined body enables it to swim swiftly; it also tucks its feet
to the side while swimming, making it faster by decreasing water resistance.
Crocodiles have webbed feet which, though not used to propel them through the
water, allow them to make fast turns and sudden moves in the water or initiate
swimming. Webbed feet are an advantage in shallower water where the animals
sometimes move around by walking. Crocodiles have a palatal flap, a rigid tissue at the back of the mouth that
blocks the entry of water. The palate has a special path from the nostril to the glottis that bypasses the mouth. The nostrils are closed during submergence.
A crocodile’s physical traits allow it to be a successful predator. Its external morphology is a sign of its aquatic and predatory lifestyle. Its streamlined body enables it to swim swiftly; it also tucks its feet
to the side while swimming, making it faster by decreasing water resistance.
Crocodiles have webbed feet which, though not used to propel them through the
water, allow them to make fast turns and sudden moves in the water or initiate
swimming. Webbed feet are an advantage in shallower water where the animals
sometimes move around by walking. Crocodiles have a palatal flap, a rigid tissue at the back of the mouth that
blocks the entry of water. The palate has a special path from the nostril to the glottis that bypasses the mouth. The nostrils are closed during submergence.
BEHAVIOUR & DIET
Crocodiles are ambush predators, waiting for fish or land animals to come close, then
rushing out to attack. Crocodiles mostly eat fish, amphibians, crustaceans, molluscs, birds, reptiles, and mammals, and they occasionally cannibalize smaller crocodiles. What a crocodile eats varies
greatly with species, size and age. From the mostly fish-eating species, like
the slender-snouted and freshwater crocodiles, to the larger species like the Nile crocodile and the saltwater crocodile that prey on large mammals, such as buffalo, deer and wild boar, diet shows great diversity. Diet is also greatly affected
by the size and age of the individual within the same species. All young crocodiles
hunt mostly invertebrates and small fish, gradually moving on to larger prey. Being ectothermic (cold-blooded) predators, they have a very slow metabolism, so they can survive long periods without food
REPRODUCTION
Crocodiles lay eggs, which are laid in either holes or mound nests, depending on species. A hole nest is usually excavated in
sand and a mound nest is usually constructed out of vegetation. Nesting periods range from a few weeks up to six months. Courtship takes place in a series of behavioural interactions
that include a variety of snout rubbing and submissive display that can take a
long time. Mating always takes place in water, where the pair can be observed
mating several times. Females can build or dig several trial nests which appear
incomplete and abandoned later. The egg are hard shelled, but translucent at
the time of egg-laying. Depending on the species of crocodile, 7 to 95 eggs are
laid. Crocodile embryos do not have sex chromosomes, and unlike humans, sex is
not determined genetically. Sex is determined by temperature.


Komentar
Posting Komentar